
#Basic accounting principles professional
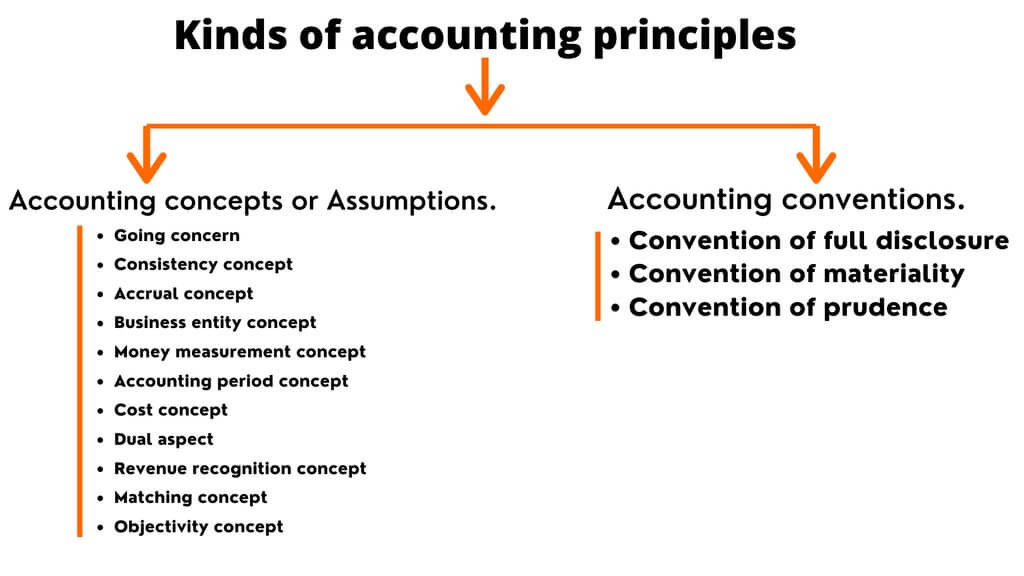
They also draw on established best practices governing cost, disclosure, matching, revenue recognition, professional judgment, and conservatism. These 10 guidelines separate an organization's transactions from the personal transactions of its owners, standardize currency units used in reports, and explicitly disclose the time periods covered by specific reports. GAAP consists of these three parts: Basic Accounting Principles and Guidelines Without GAAP, accountants could use misleading methods to paint a deceptive picture of a company or organization's financial standing. These components create consistent accounting and reporting standards, which provide prospective and existing investors with reliable methods of evaluating an organization's financial standing. GAAP incorporates three components that eliminate misleading accounting and financial reporting practices: 10 accounting principles, FASB rules and standards, and generally accepted industry practices. Read about compliance officers What Are the Basic Principles of Accounting? The consistency of GAAP compliance also allows companies to more easily evaluate strategic business options. External parties can easily compare financial statements issued by GAAP-compliant entities and safely assume consistency, which allows for quick and accurate cross-company comparisons.īecause GAAP standards deliver transparency and continuity, they enable investors and stakeholders to make sound, evidence-based decisions. GAAP compliance makes the financial reporting process transparent and standardizes assumptions, terminology, definitions, and methods.

law requires businesses releasing financial statements to the public and companies publicly traded on stock exchanges and indices to follow GAAP guidelines. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) uses GAAP as the foundation for its comprehensive set of approved accounting methods and practices. Generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, are standards that encompass the details, complexities, and legalities of business and corporate accounting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
